
stomach model Anatomy models labeled, Anatomy models, Human anatomy and physiology
22: Digestive System 22.6: The Stomach
Gastrointestinal Digestive System and Labels Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
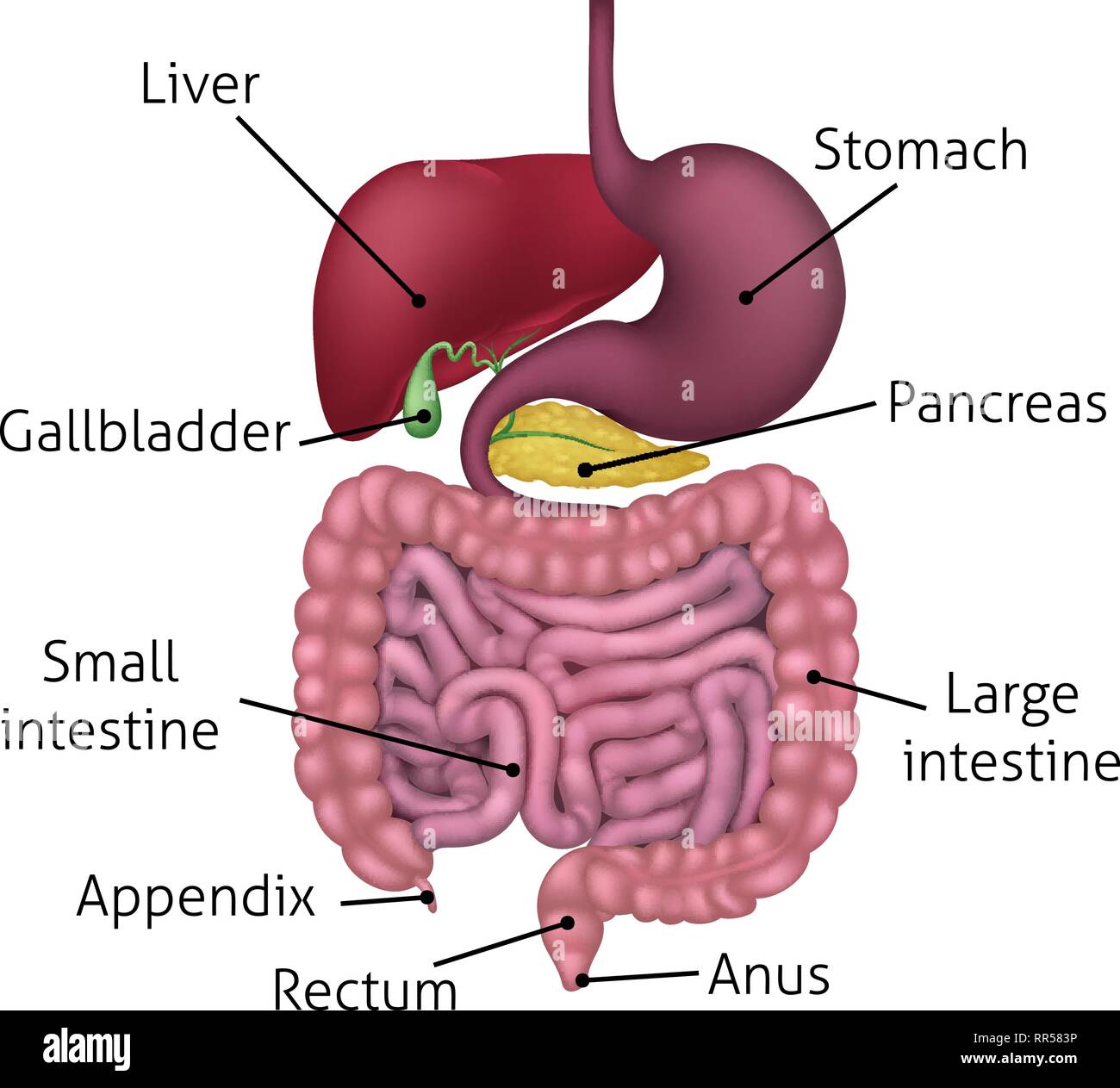
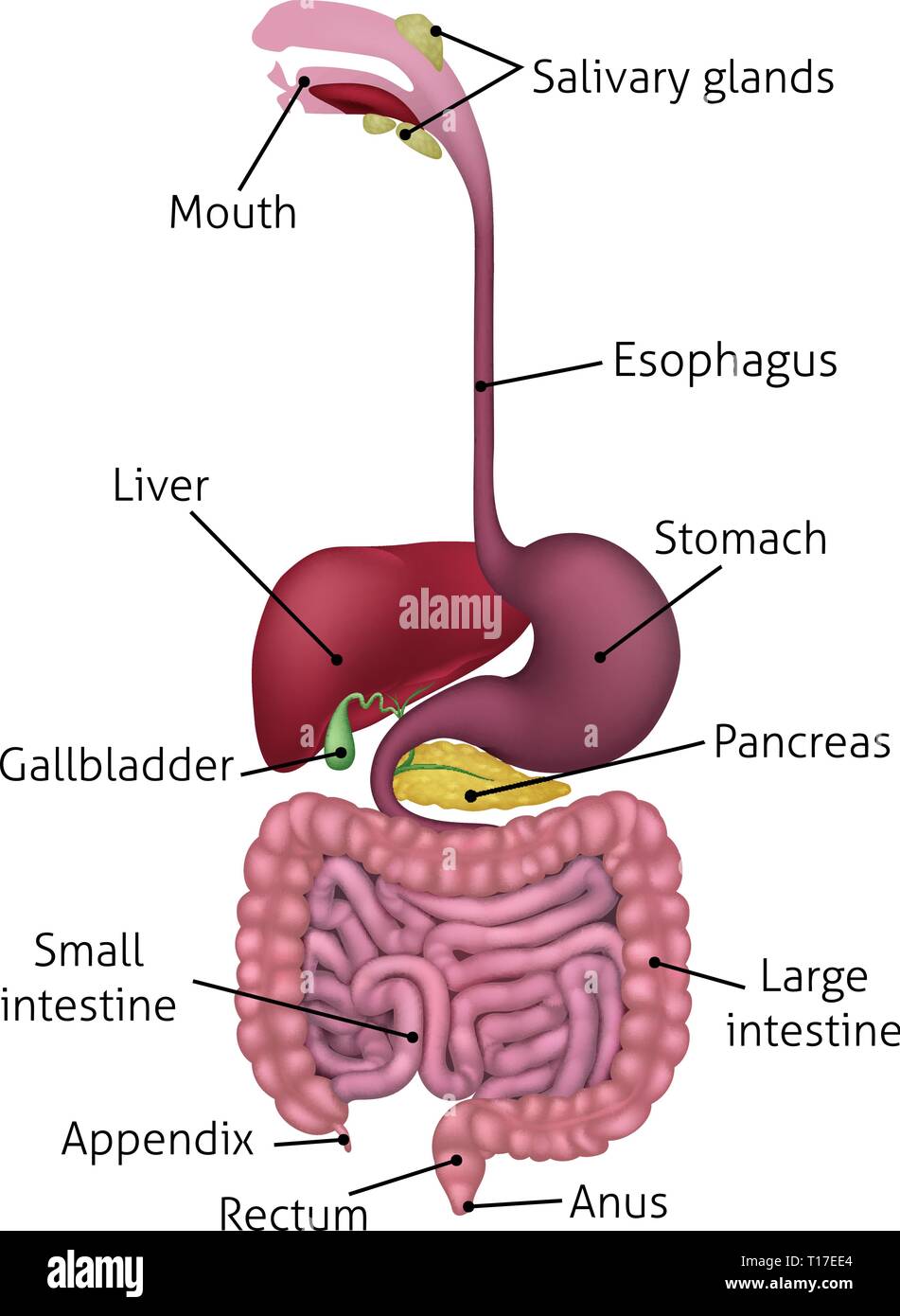
Diagram Stomach Gallbladder Liver Pancreas Small intestine Large intestine How they interact Common problems Summary The stomach is located in the upper part of the abdomen. The digestive.
How is the shape of the stomach?(a) As V(b) As J(c) As O(d) None of the above
Picture of Abdomen. The abdominal cavity is the part of the body that houses the stomach, liver, pancreas, kidneys, gallbladder, spleen, and the large and small intestines. The diaphragm marks the top of the abdomen and the horizontal line at the level of the top of the pelvis marks the bottom. Connective tissue called the mesentery holds the.

Stomach Diagram Anatomy koibana.info Stomach diagram, Digestive system anatomy, Stomach
The stomach is a muscular organ that is found in our upper abdomen. If we were to locate it on our bodies, it can be found on our left side just below the ribs. In simple terms, the stomach is a kind of digestive sac. It is a continuation of the esophagus and receives our churned food from it. Therefore, the stomach serves as a kind of.
Labeled Digestive System
The main bones in the abdominal region are the ribs. The rib cage protects vital internal organs. There are 12 pairs of ribs and they attach to the spine. There are seven upper ribs, known as.

The Stomach Organs Parts, Anatomy, Functions of the Human Stomach
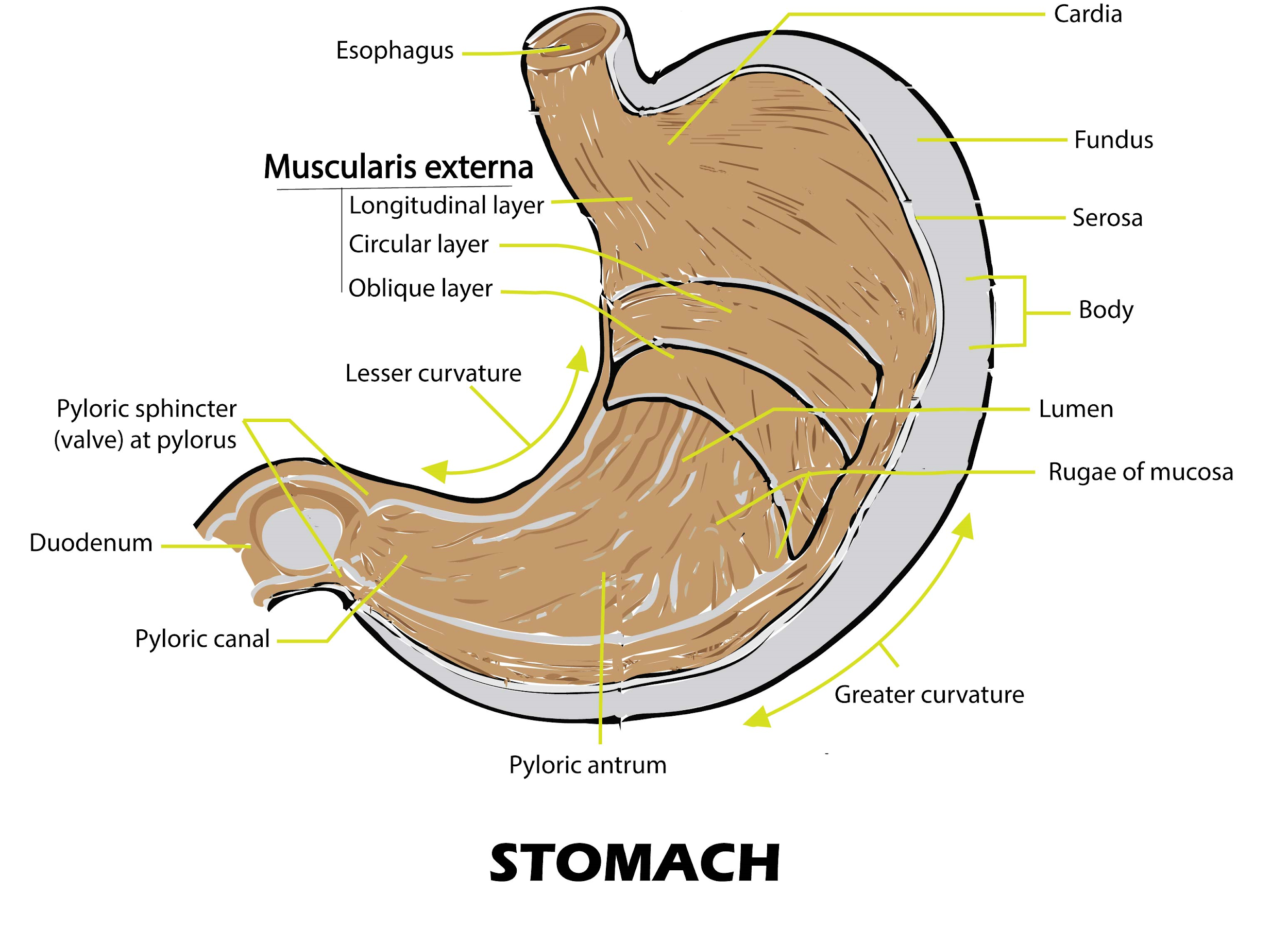
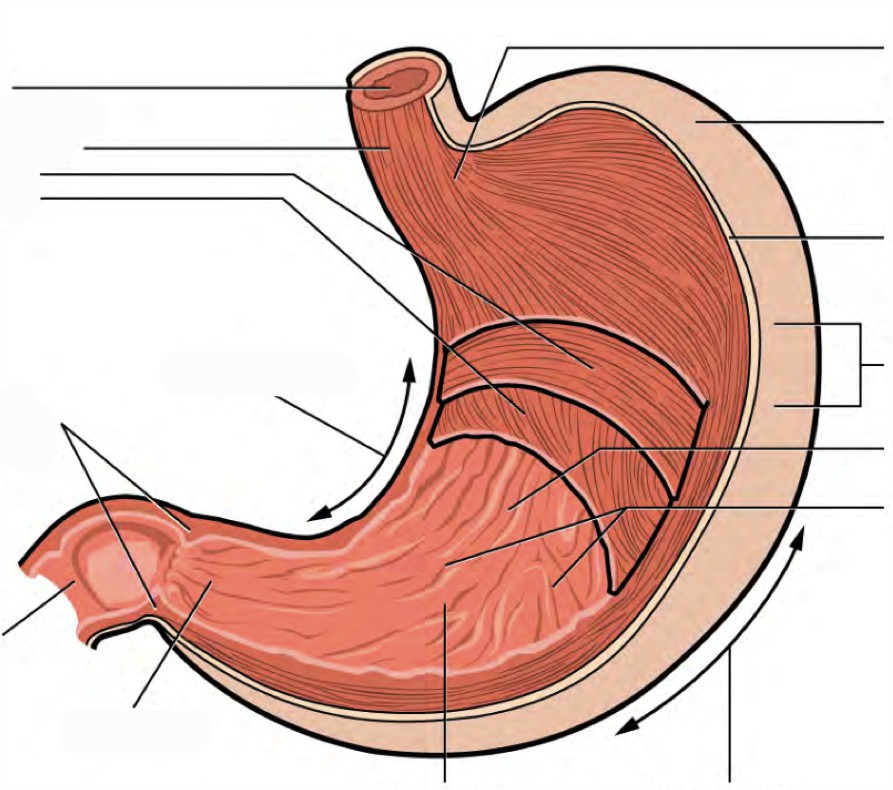
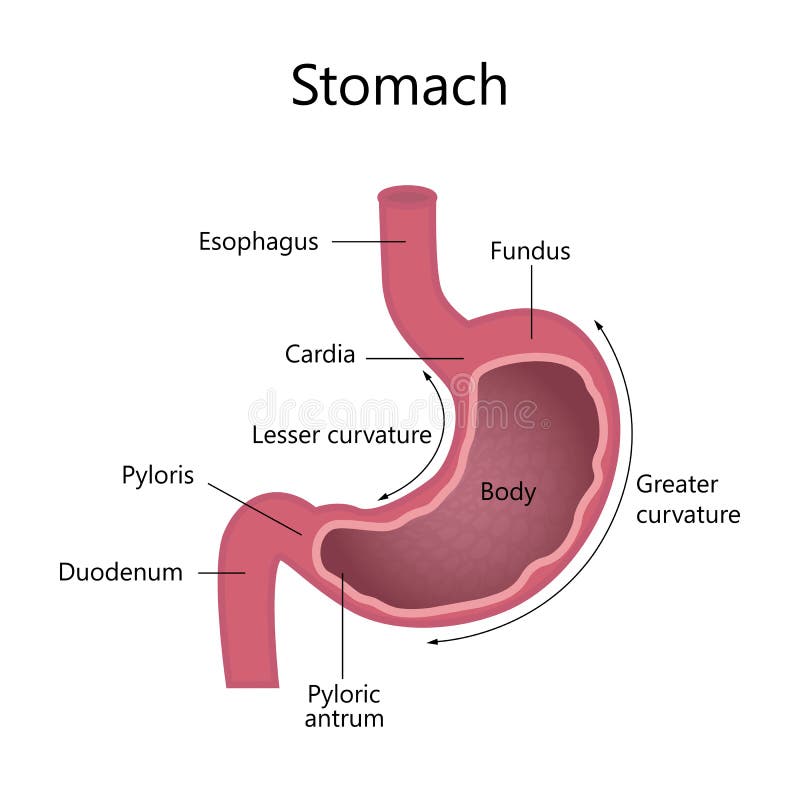
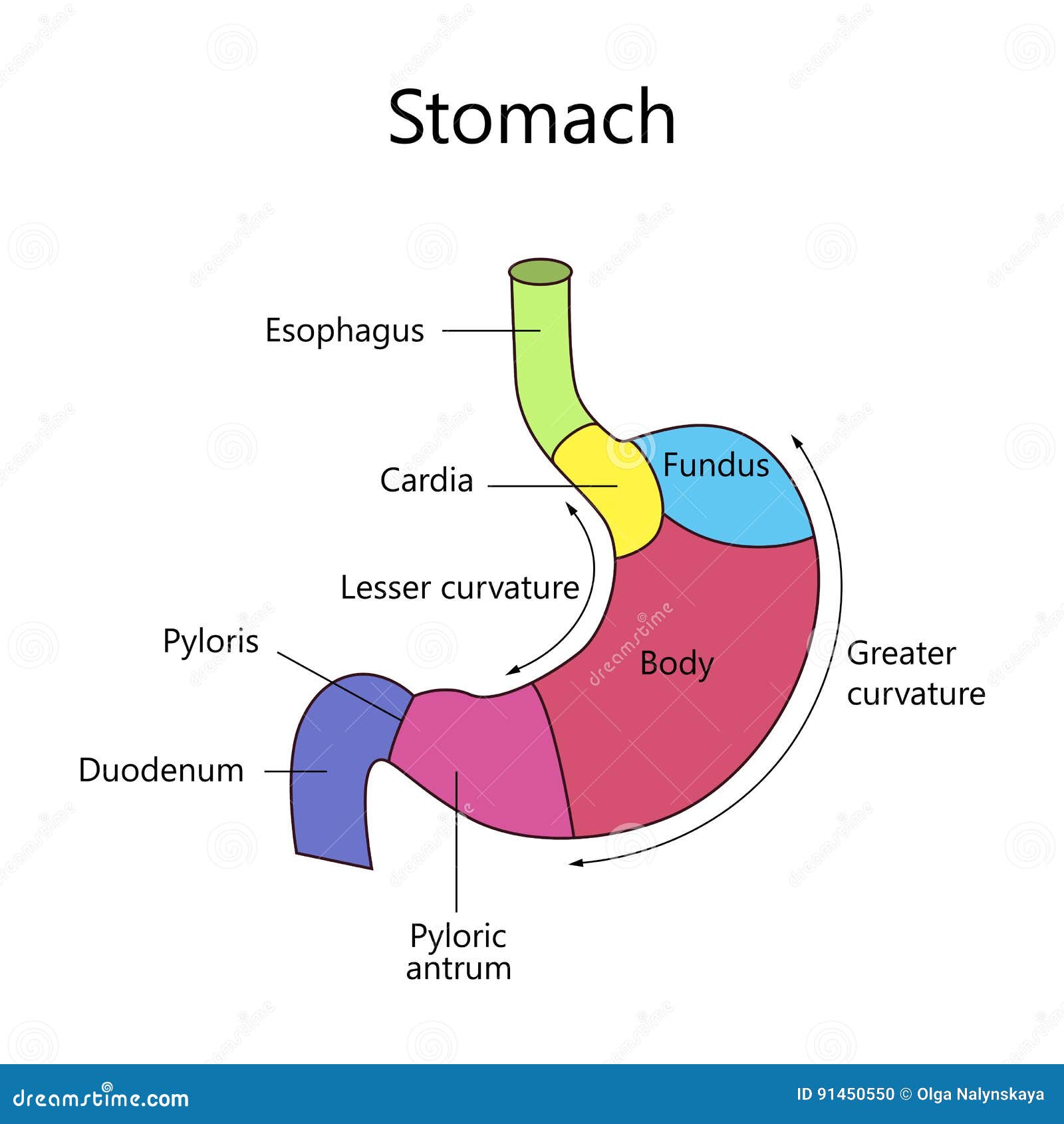
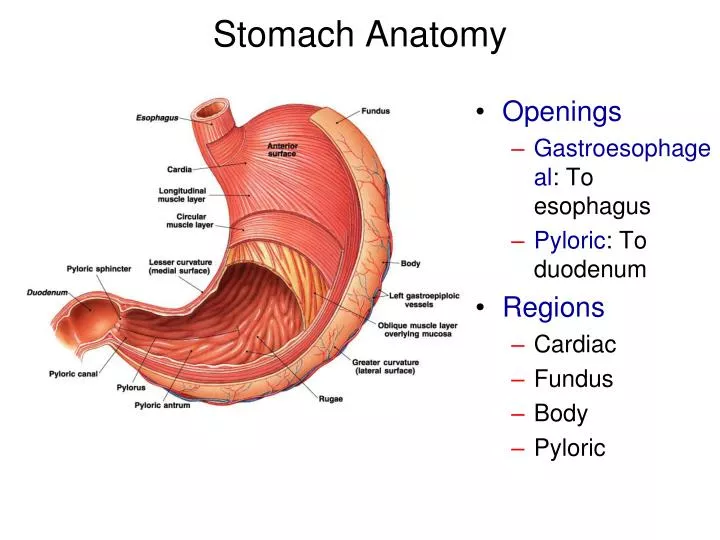
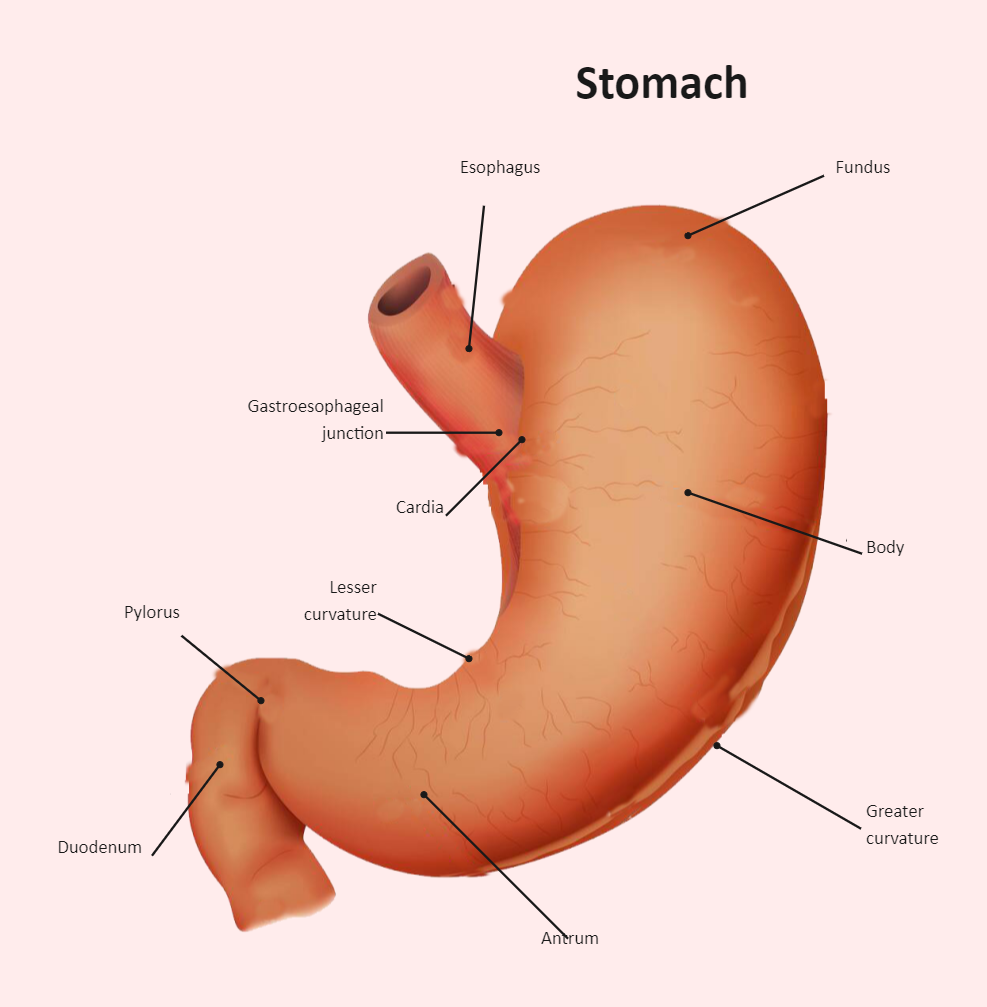
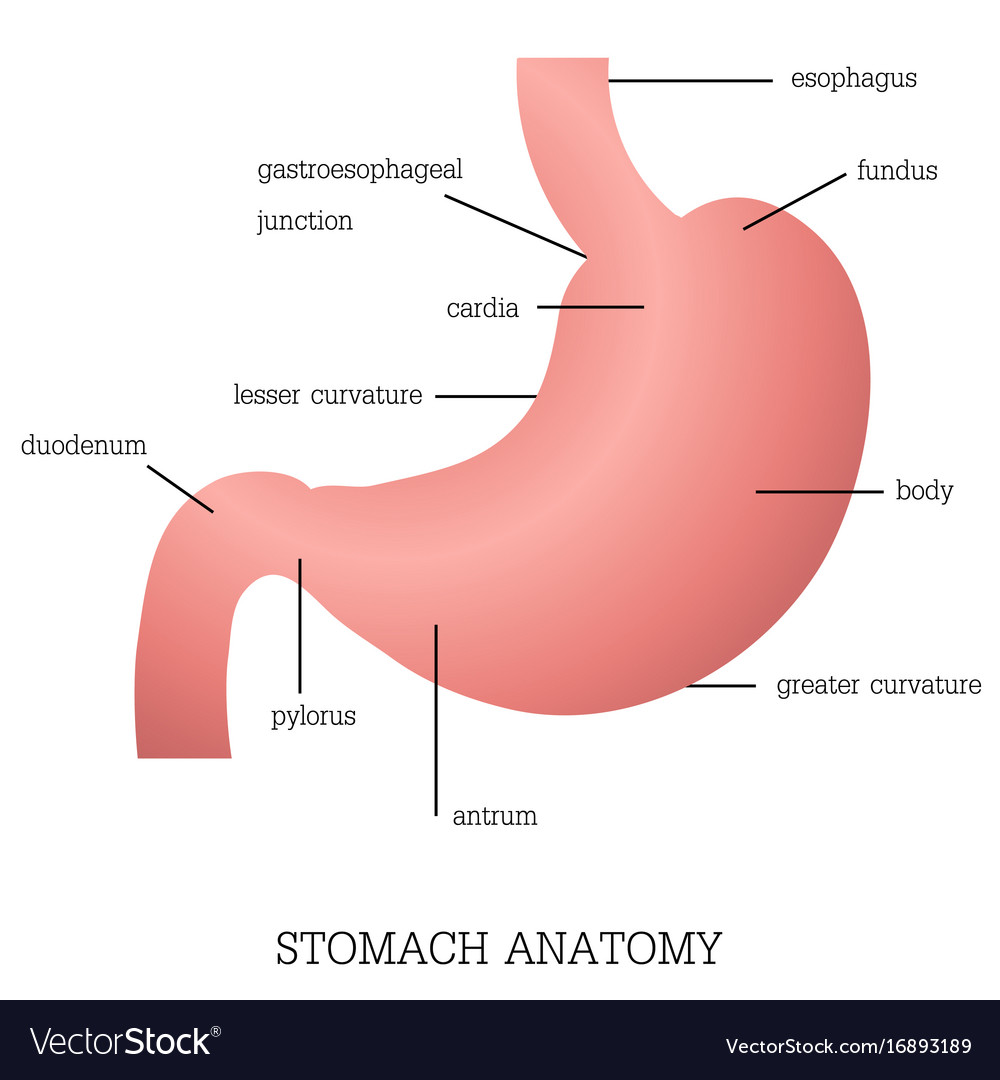
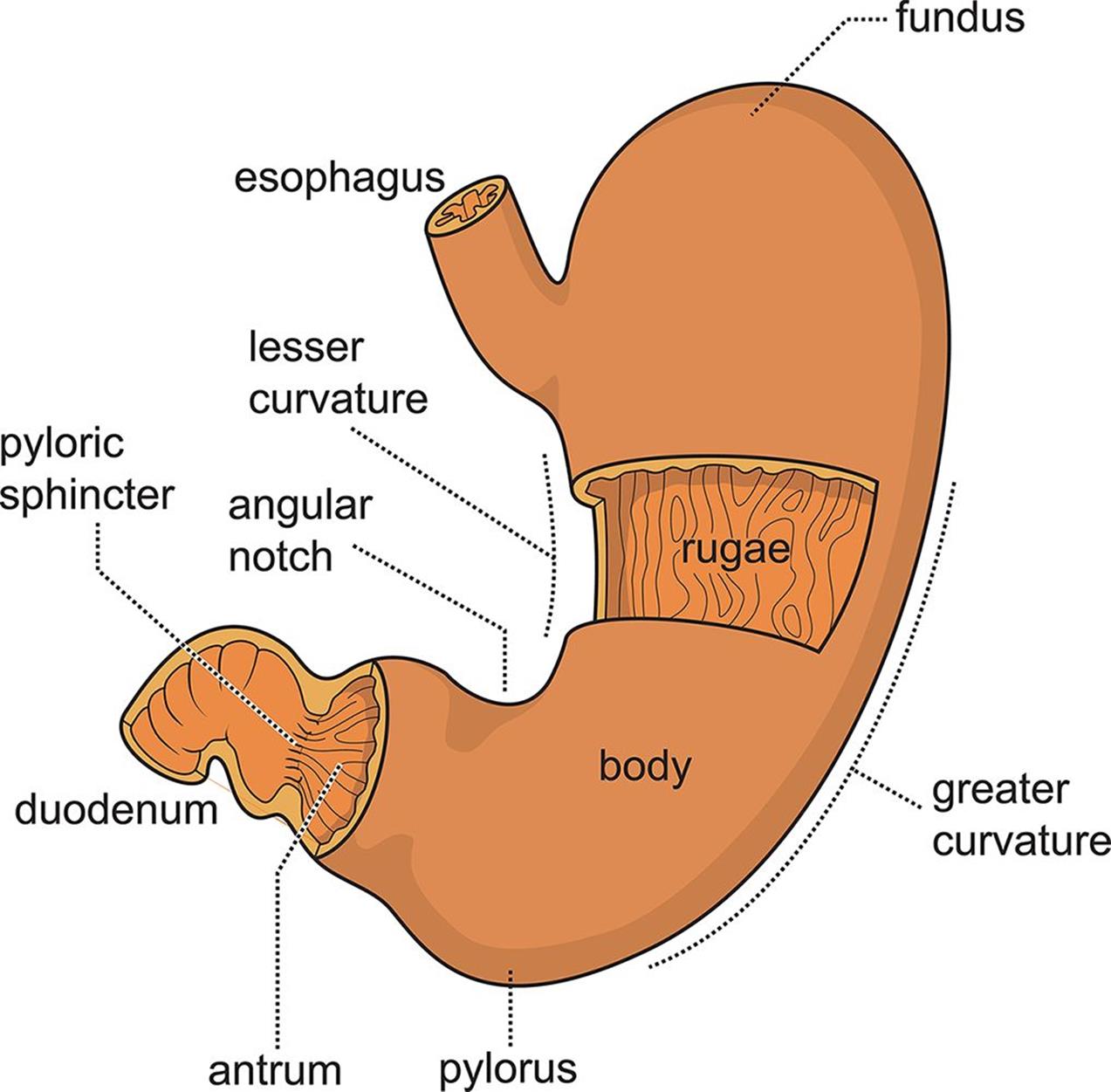
The stomach has four main anatomical divisions; the cardia, fundus, body and pylorus: Cardia - surrounds the superior opening of the stomach at the T11 level. Fundus - the rounded, often gas filled portion superior to and left of the cardia. Body - the large central portion inferior to the fundus. Pylorus - This area connects the.
PreLab 8 Human Anatomy Lab Manual
Anatomy of the Stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper belly (abdomen). It's part of the digestive system. It's between the end of the food pipe (esophagus) and the start of the first part of the small bowel (duodenum). The stomach is much like a bag with a lining. The stomach is made of these five layers: Mucosa.
Internal Structure Human Stomach Stock Vector Illustration of medicine, healthy 91532703
The stomach has four major regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. The addition of an inner oblique smooth muscle layer gives the muscularis the ability to vigorously churn and mix food. The convex lateral surface of the stomach is called the greater curvature; the concave medial border is the lesser curvature.
Internal Structure Human Stomach Stock Vector Illustration of medical, antrum 91450550
The stomach is a key part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, sitting between the esophagus and duodenum. Its functions are to mix food with stomach acid and break food down into smaller particles using chemical and mechanical digestion. The stomach can perform these roles due to the layers of the stomach wall.

Anatomy 501 > Sorrells > Flashcards > Stomach, Spleen, and Small Intestine StudyBlue
The stomach is a sac-like organ with strong muscular walls. In addition to holding food, it serves as the mixer and grinder of food. The stomach secretes acid and powerful enzymes that continue.

Human Stomach Anatomy Vector Illustration With Labels Stock Illustration Download Image Now
Label on a diagram the four main regions of the stomach, its curvatures, and its sphincter Identify the four main types of secreting cells in gastric glands, and their important products Explain why the stomach does not digest itself Describe the mechanical and chemical digestion of food entering the stomach

The Stomach Organs Parts, Anatomy, Functions of the Human Stomach
The pylorus is surrounded by a thick circular muscular wall that is normally tonically constricted, forming a functional (if not anatomically discrete) pyloric sphincter that controls the movement of chyme. 22.6B: Microscopic Anatomy of the Stomach is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
Anatomy Of Stomach And Esophagus
This online quiz is called Label the Stomach . It was created by member bloomerwirchball and has 15 questions.
Stomach Diagram Labeled EdrawMax Template
There are four main regions in the stomach: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus (Figure 21.4.1 21.4. 1 ). The cardia (or cardiac region) is the point where the esophagus connects to the stomach and through which food passes into the stomach. Located inferior to the diaphragm, above and to the left of the cardia, is the dome-shaped fundus.
Structure and function of stomach anatomy system Vector Image
Anatomy of the Stomach. The stomach is an organ of the digestive system. It is an expanded section of the digestive tube between the esophagus and small intestine. Its characteristic shape is well known. The right side of the stomach is called the greater curvature and the left the lesser curvature. The most distal and narrow section of the.
Parts Of Stomach
The stomach is an organ of the digestive system, specialized in the accumulation and digestion of food. Its anatomy is quite complex; it consists of four parts, two curvatures and receives its blood supply mainly from the celiac trunk. Innervation is provided via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus .